Periodontal disease known as periodontitis alongside dental caries is the main factor of teeth loss.
What we have to know about periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is a complex disease, both in terms of the underlying causes of its appearance, the poor symptoms in the early stages, multiple favoring factors, often hard to avoid, and, especially, the speed of evolution from treatable stages to stages where treatment can only stop evolution.
Undiagnosed and untreated it evolves rapidly with devastating effects on patients, both on physically and emotionally levels.
Names under which periodontal disease it is known
Periodontal disease is known by various names, gaining an “appropriate reputation” due to the evolution and effects on patients:
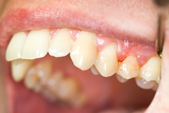 Periodontitis: most commonly popular term used for periodontal disease;
Periodontitis: most commonly popular term used for periodontal disease;
“The disease of healthy teeth “: very often the disease appears and progresses without visible effects on the teeth (dental caries) and patients don’t think is necessary a visit to the dentist;
“The silent killer”: acts very quickly and without visible effects, from the first stages of development to advanced stages, with aggressive forms of manifestation. Without an accurate diagnosis and treatment it leads often to teeth loss.
How does the periodontal disease begin?
Periodontal Disease is caused by the pathogen bacteria from the bacterial plaque (bio-film) which adheres on teeth or gums.
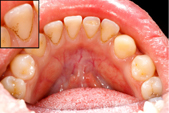 Not removed by daily brushing (2 times per day), the bacterial plaque mineralizes, resulting in the appearance of dental tartar, that can be removed only by professional cleaning in the dental office (recommended 2 times per year).
Not removed by daily brushing (2 times per day), the bacterial plaque mineralizes, resulting in the appearance of dental tartar, that can be removed only by professional cleaning in the dental office (recommended 2 times per year).
By accumulating, dental tartar acts mechanically on the gums, having a cumulative double negative effect:
• inflammation of the gums (gingivitis, the first stage of periodontal disease – bleeding gums)
• removal of the gums from the teeth (gingival retraction) that favors periodontal disease progression. Left untreated, leads most often to teeth loss.
Development stages of periodontal disease
In the specialty literature, for stages of developing of periodontal disease are used multiple classifications.
For a better understanding we will use a split into two complex parts, each of it with sub-phases of evolution, which may differ from patient to patient:
Gingivitis:
• First stage of progression of periodontal disease;
• Starts with gums inflammation;
• Other symptoms: bleeding gums;
• Most often ignored by patients;
• Can be discovered and treated by medical specialists in close collaboration with the patient.
Periodontitis
• Second stage of progression of periodontal disease;
• Gum inflammation and bone support loss around the tooth;
• Other symptoms : bleeding gums at the slightest touch, the occurrence of periodontal pockets, tooth mobility;
• Untreated leads to teeth loss;
• Very aggressive forms for young people.
Favoring factors of occurrence and progression of periodontal disease
• Incomplete oral hygiene;
• Crooked teeth (misalignment in the arcade);
• Improper development of the jaws (open bite, reverse or deep bite);
• Smoking;
• Various diseases of the body: diabetes;
• Unbalanced food diets;
• Genetic predisposition;
• Stress which causes the decrease of the immune system.
Symptoms of periodontal disease
• Unpleasant taste in the mouth and bad breath;
• Inflammation of the gums (bright red color);
• Bleeding gums;
• Teeth with withdrawn gums;
• Painful mastication;
• Dental sensitivity to cold, hot, sweet, sour;
• Mobile teeth.
Treatment of the periodontal disease
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, to achieve complete oral rehabilitation are required treatment schemes that include various periodontal procedures, surgery, implantology and dental aesthetics.
Articles of interest:
Periodontitis a disease that can be prevented.
Complex treatment schemes for periodontitis
If you are affected by periodontitis and you want restore functional and aesthetic aspects of teeth, Schedule Now a detailed consultation!



